The National Health Service (NHS) plays a vital role in providing quality healthcare to millions of people in the United Kingdom. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, innovative solutions are being implemented to enhance patient care and safety. One such advancement is the use of segregation and isolation pods, which have become increasingly significant in managing infectious diseases and other health conditions. This post explores how these pods are revolutionising patient care within the NHS.
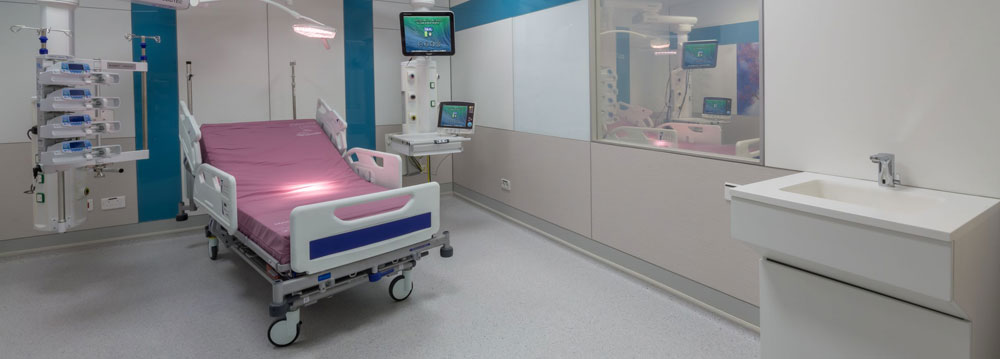
Enhancing Infection Control:
Infection control is of utmost importance within healthcare settings, especially when dealing with highly contagious diseases. Segregation and isolation pods offer a dedicated and controlled environment to minimise the risk of disease transmission. These pods are designed to isolate infected patients, preventing the spread of pathogens to other patients, healthcare workers, and visitors. By creating a physical barrier between individuals, these pods effectively reduce the chances of cross-contamination, ensuring the safety of everyone involved.
Optimising Resource Utilisation:
Isolation pods also help optimise resource utilisation within the NHS. By confining infectious patients to dedicated spaces, healthcare facilities can efficiently allocate staff, equipment, and supplies necessary for their care. Segregation pods can be equipped with specialised ventilation systems, negative air pressure, and other advanced technologies to ensure proper containment and airflow management. This targeted approach enables healthcare providers to deliver focused care while efficiently utilising limited resources, enhancing overall patient outcomes.
Facilitating Personalised Care:
Patients requiring isolation often face challenges in receiving personalised care due to physical separation from healthcare professionals. However, segregation and isolation pods are designed with patient comfort and well-being in mind. These pods are equipped with features such as communication systems, video conferencing capabilities, and medical device integration, allowing healthcare providers to remotely interact and monitor patients. By facilitating direct and continuous communication, healthcare professionals can address patient concerns, provide emotional support, and ensure the delivery of personalised care despite the physical isolation.
Supporting Vulnerable Populations:
Certain patient groups, such as those with weakened immune systems, are particularly susceptible to infections. Segregation and isolation pods offer a safe and controlled environment for vulnerable patients, shielding them from potential harm. Additionally, these pods can be customised to meet the specific needs of different patient populations. For instance, pediatric isolation pods can be designed with child-friendly aesthetics and play areas, easing anxiety and creating a more positive experience for young patients. By tailoring the environment to individual requirements, segregation pods contribute to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Preparing for Future Outbreaks:
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a wake-up call for healthcare systems worldwide, emphasising the need for robust measures to combat infectious diseases. Segregation and isolation pods have proven to be valuable tools in managing outbreaks and containing the spread of infections. The lessons learned from this crisis have highlighted the importance of investing in such infrastructure and preparedness. By incorporating segregation and isolation pods into healthcare facilities, the NHS is better equipped to respond swiftly and effectively to future outbreaks, safeguarding public health and minimising disruptions to healthcare services.
Segregation and isolation pods can seamlessly integrate with telemedicine and remote monitoring technologies, further improving patient care within the NHS. By connecting patients in isolation with healthcare professionals through video conferencing and remote monitoring devices, medical professionals can closely monitor vital signs, provide real-time medical advice, and conduct virtual consultations. This integration not only reduces the risk of disease transmission but also allows for timely interventions and continuous care. Patients can receive expert guidance without leaving the safety of their isolation pods, minimising the need for physical contact and ensuring ongoing medical support.
Psychosocial Support and Mental Well-being:
Isolation can have a significant impact on patients’ mental well-being and overall psychosocial health. The design of segregation and isolation pods within the NHS incorporates elements that prioritise patients’ emotional needs. These pods can be equipped with entertainment systems, access to the internet, and virtual connectivity to loved ones. Furthermore, mental health support services can be readily available, providing counseling and therapy sessions remotely. By addressing the psychosocial aspects of care, segregation and isolation pods promote a holistic approach to patient well-being, supporting their mental resilience and aiding in the overall healing process.
Training and Preparedness:
The introduction of segregation and isolation pods in the NHS also necessitates specialised training for healthcare professionals. Staff members require comprehensive training on infection control protocols, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and efficient utilisation of the pod’s resources and technology. By investing in training programs, the NHS ensures that healthcare workers are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to deliver safe and effective care within these specialised environments. This training also enhances preparedness for future outbreaks or pandemics, enabling healthcare professionals to respond swiftly and confidently to emerging challenges.
Collaboration and Research Opportunities:
The implementation of segregation and isolation pods in the NHS creates opportunities for collaboration and research. These pods provide controlled environments for conducting studies on infectious diseases, transmission patterns, and treatment strategies. By utilising the data collected within the pods, researchers can gain valuable insights into disease management and prevention. Collaboration with academic institutions, public health agencies, and other healthcare organisations can foster innovation, leading to advancements in isolation pod design, infection control protocols, and overall patient care practices.
Segregation and isolation pods have become indispensable tools in the NHS, supporting patient care through enhanced infection control, resource utilisation, and personalised support. Integration with telemedicine, remote monitoring, and mental health services further elevates the level of care provided within these specialised environments. As the NHS continues to embrace advancements in healthcare, segregation and isolation pods not only strengthen the response to infectious diseases but also lay the foundation for a more resilient and patient-centered healthcare system.